In an increasingly data-driven world, professionals specialising in managing, analysing, and interpreting information play a key role (and are very well paid). Within this ecosystem, a variety of data-related careers have emerged, each with its own specific responsibilities and demands.
Before we explore what characterises each of these careers, let's understand the current scenario and prospects for the evolution of these various options, particularly due to the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
What is the world of data like today?
In recent years, we've seen a constant growth in the demand for qualified professionals, and often there aren't enough people available on the market to meet this demand. These circumstances lead companies to import labour from larger, less developed countries such as Brazil, India and China. This trend began in the 2000s and we can see it all over Europe today.
As a result, we have seen continued growth and many opportunities in technology careers, especially in data, given the growing value of information. To quote the famous Forbes article: “The world's most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data. Data is the new oil”.
What is the role of Artificial Intelligence?
The trending topic of the moment is already changing the way technology professionals work, and in the area of data it couldn't be any different. AI should not be feared but used as a productivity tool to develop more efficient and intelligent solutions for business.
In this case, we're going to understand how ChatGPT can be incorporated into data work, enhancing it:
-
Complete or format code in different languages
It is humanly impossible for a professional to know how to use all the language features at once. So, this tool can help you complete code or set up templates to make your work easier.
Prompt example: “Assemble a template to create a dataframe in python from a csv file”.
-
Analyse errors
When developing a solution, errors occur and often the messages displayed are confusing or don't give the full context. Use AI to understand what may have caused the problem.
Prompt example: “Explain the error ‘Ambiguous Column Name’ in SQL Server”.
-
Learn new features
Often, the explanation generated by AI on a given topic can be clearer than many tutorials on YouTube. Use the tool to learn new codes.
Prompt example: “Explain how to use the ‘dbutils.fs.rm’ command in databricks”.
-
Generate templates for common problems
Programming in any language can be a repetitive task. It is possible to generate templates that can be useful in various cases and save time.
Prompt example: “Generate a template to calculate the r square of two variables in Scala”.
With these tips, it's clear that AI won't replace data professionals, but it will complement their work and make it more efficient.
Data careers
Let's now explore and understand how data careers are divided, highlighting the profile of each professional and the importance of their role in effective information management. We'll talk about the following data careers:
-
Data Analyst / Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst
-
Data Engineer
-
Data Scientist
-
Data Architect
-
Tech Lead
Data Analyst / Business Intelligence Analyst
A Data Analyst or Business Intelligence Analyst is a specialist in collecting, analysing and presenting data to help organisations make strategic decisions. Their responsibilities include:
- Collecting data;
- Cleansing and transforming information;
- Creating reports and dashboards;
- Supporting decision-making.
The Data Analyst needs to master BI tools, have analytical skills, programming knowledge and a solid understanding of business objectives.
The radar chart below illustrates the main competences of a Data Analyst:
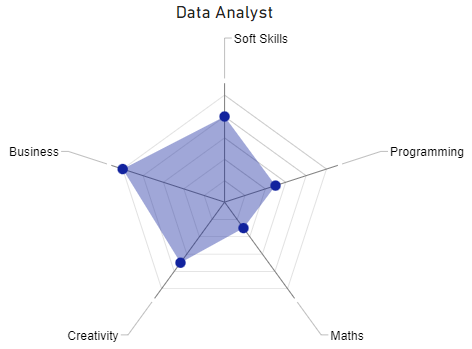
Data Engineer
A Data Engineer is a specialist in managing and optimising an organisation's data infrastructure. Their responsibilities include:
- Creating and maintaining data pipelines;
- Integrating a variety of data sources;
- Ensuring data quality;
- Information security.
To succeed in this career, it is essential to have advanced knowledge of programming languages, databases, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools, as well as an in-depth understanding of the organisation's business context. With the growing demands for data management, Data Engineers have solid career prospects and are key players in the governance and effective use of data.
The radar chart below illustrates the core competences of a Data Engineer:
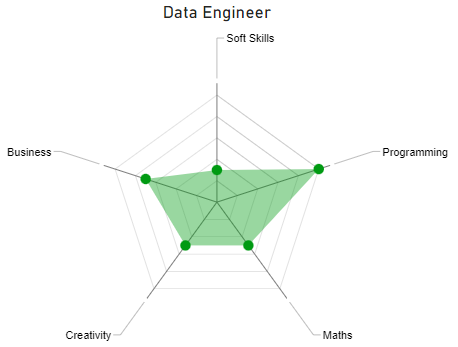
Data Scientist
A Data Scientist is a highly qualified professional who excels at analysing complex data to extract meaningful insights and guide an organisation's strategies. Their responsibilities include:
- Collecting, cleansing and processing data;
- Developing predictive and prescriptive models;
- Creating Machine Learning (ML) algorithms;
- Presenting results in an accessible way.
Proficiency in programming languages, statistics, Machine Learning and a solid understanding of business objectives are essential. With high-potential career prospects, Data Scientists are key players in transforming data into strategic insights to drive the success of organisations.
The radar chart below illustrates the core competences of a Data Scientist:
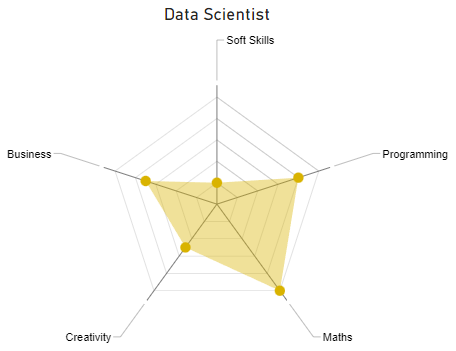
Data Architect
A Data Architect is a specialist in planning and designing an organisation's data infrastructure. Their responsibilities include:
- Defining storage strategies;
- Systems integration;
- Data modelling;
- Data governance.
The Data Architect plays a critical role in ensuring that data is managed efficiently, securely and in line with the company's business objectives. They need to have in-depth knowledge of database technologies, data architecture, information security and a solid understanding of specific business needs.
The radar chart below illustrates the main competences of a Data Architect:
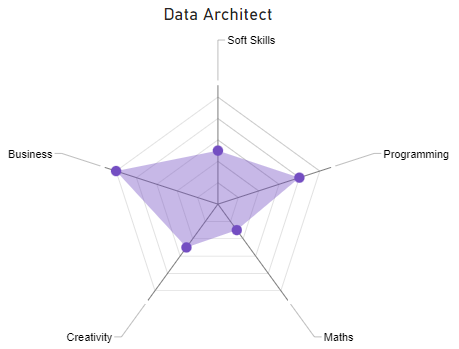
Tech Lead
A Tech Lead is a strategic leader responsible for overseeing an organisation's entire data infrastructure and related operations. Their responsibilities include:
- Development and implementation of data strategies;
- Data governance;
- Managing teams of data professionals;
- Ensuring compliance with privacy and security regulations.
Tech Leads need to possess a comprehensive vision of the company's data needs, project management, leadership and communication skills, as well as a deep knowledge of data technologies and analysis.
With the growing recognition of the importance of data in business decisions, these professionals play a critical role and have solid career prospects, often advancing to executive positions such as Chief Data Officer (CDO).
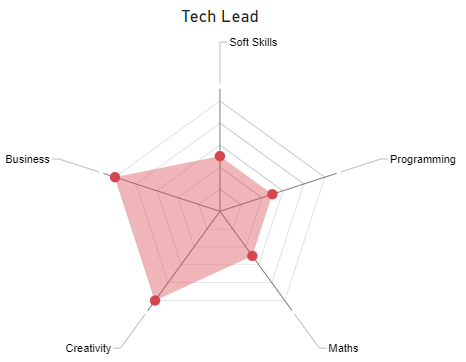
The radar chart below illustrates the main competences of a Tech Lead:
Conclusion
There are many other paths that a professional can choose to follow, and it is often necessary to have characteristics from more than one career. After all, these disciplines often intertwine and complement each other. It is not uncommon to find individuals who fulfill hybrid roles, such as a Data Analyst/Engineer or a Data Architect/Scientist.
In the modern business world, roles are not always rigidly defined: there is room for flexibility and for adapting to constantly evolving demands. Adapting to Artificial Intelligence is a good example of this: data professionals have to take advantage of these tools to enhance their work.
We hope this article has been informative and enlightening, helping you to better understand the challenges, diverse opportunities and paths available in the world of data-related careers in the information age.

